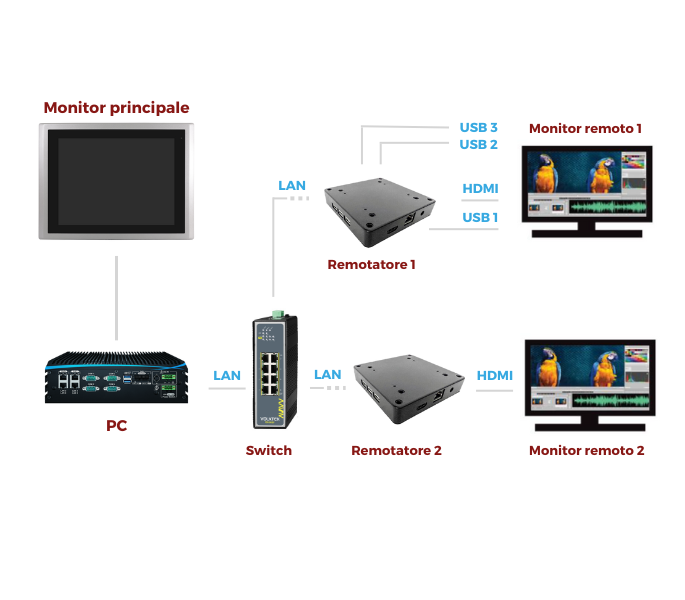
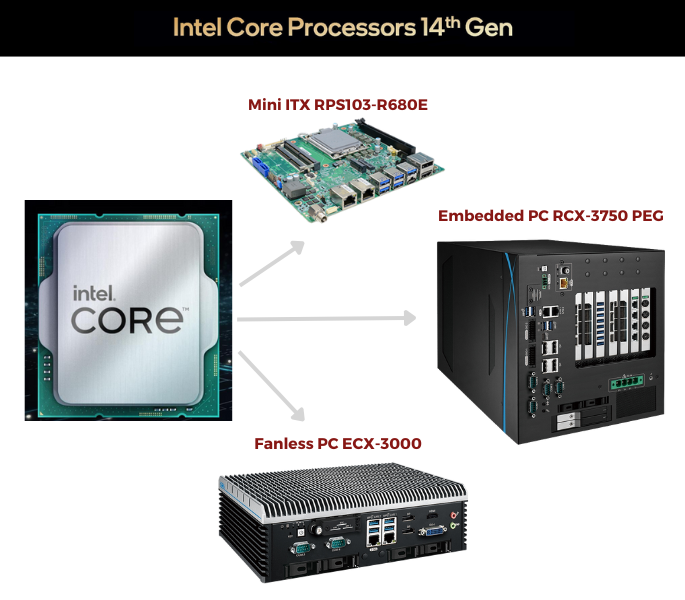
Category : News by T-Pole | 21 June 2023
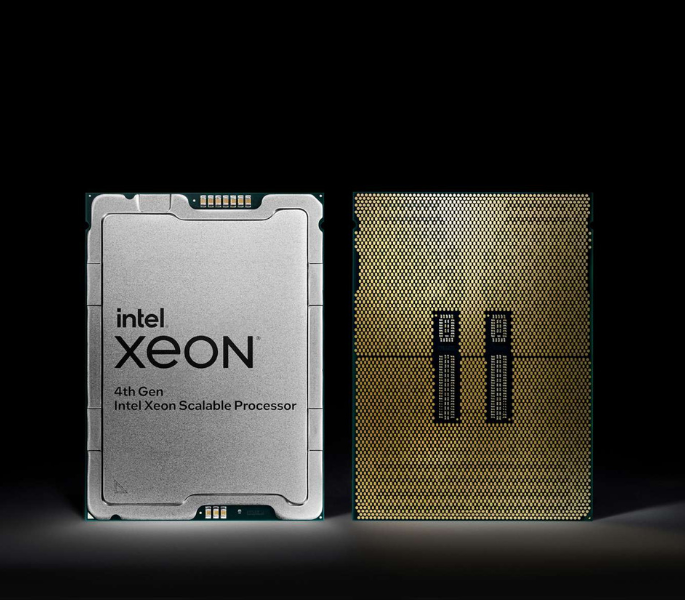
Today we present the 4th generation of scalable processors, the new generation of Xeon processors for applications that really require very high performance.
Key Point
- From 40 cores of the 3rd gen. to the 52 of the 4th gen.
- From the 6 channels of the 3th gen. DDR4 to the 8 channels DDR5 of the 4th.
- PCI Express gen 5° which has twice the bandwidth of the previous version.
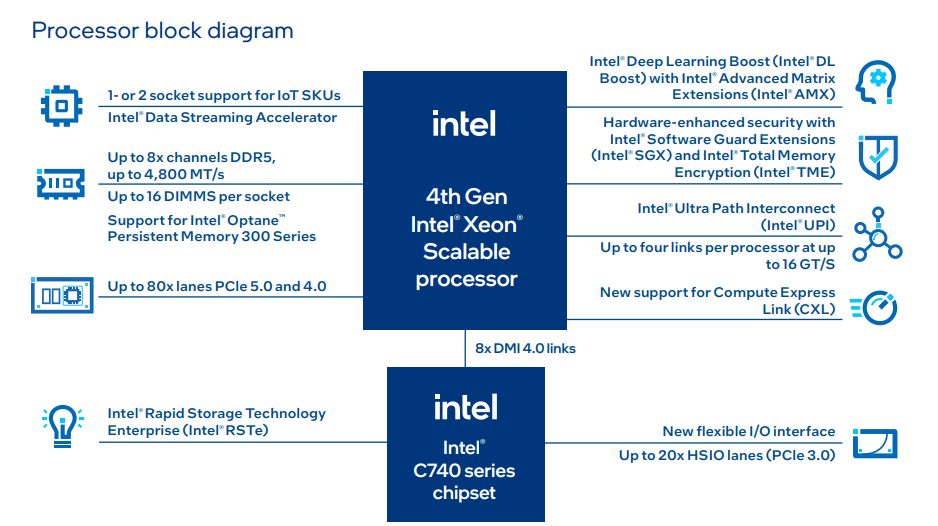
4th Generation Processors
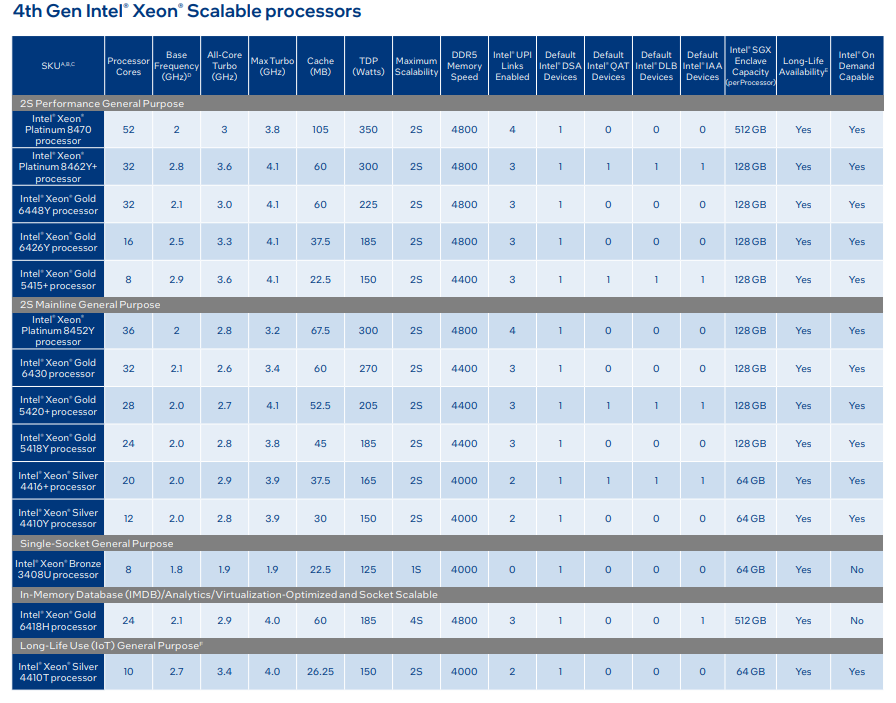
hanks to the table below it is possible to have a picture of the CPUs present in this new family and their main characteristics.
No benchmark data is yet available on CPU benchmark, at the time of writing this newsletter, but there is some really interesting information about performance on the internet.
DDR4 vs DDR5
Greater performance in terms of starting speed
DDR5 reaches 4800 MT/s while DDR4 reaches a maximum of 3200 MT/s, a 50% increase in transfer speed. With the most advanced versions of computing platforms, DDR5 expects a performance increase up to 7200 MT/s.
Reduced power means higher efficiency
At 1.1 Volt, DDR5 consumes 20% less power than the equivalent components of DDR4 at 1.2V. It not only conserves battery life in laptop computers, but also offers significant benefits for 24-hour enterprise servers. 24.
On-die ECC improves reliability
On-die Error Correction Code (ECC) is a new feature of DDR5 designed to correct bit errors within the SDRAM chip. As the density of SDRAM chips increases due to the reduction of wafer lithography, so does the potential for data loss. With on-die ECC, DDR5 reduces this risk by correcting errors within the chip, increasing reliability and reducing failure rates.
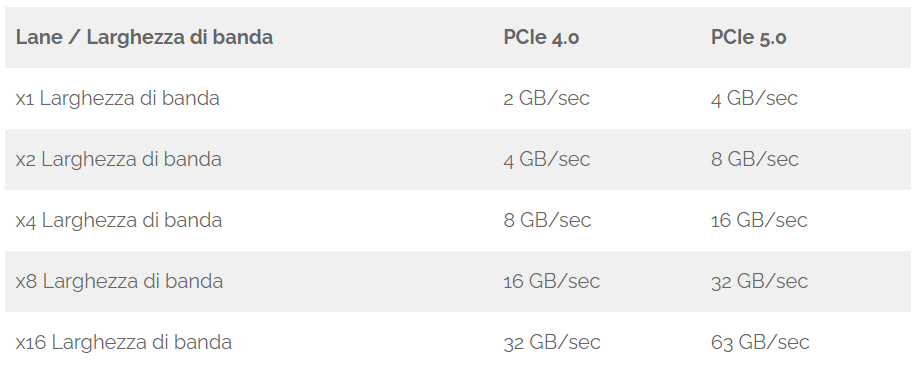
PCIe 5.0 vs 40.0
Below is a very useful summary table to really understand the implementations of this new technology dropped on the expansion sockets available in server boards.
Intel AMX
Among the countless innovations introduced by Intel on these processors we want to highlight a very interesting one for AI applications.
In fact, this significantly improves inference and training times in artificial intelligence applications.
What is AMX?
First, AMX is an accelerator that improves workload management in AI applications.
The Intel AMX extensions expand the instruction set previously available in the x86 architecture by introducing new skills and in particular optimizing the management of tensors, mathematical structures at the basis of processing in the field of artificial intelligence.
Intel® AMX adds in particular two new elements: a series of two-dimensional registers (tiles) and a set of accelerators capable of operating on these registers. These accelerators share memory access consistently with the rest of the CPU elements and can work synchronously with and in parallel with other x86 execution units.
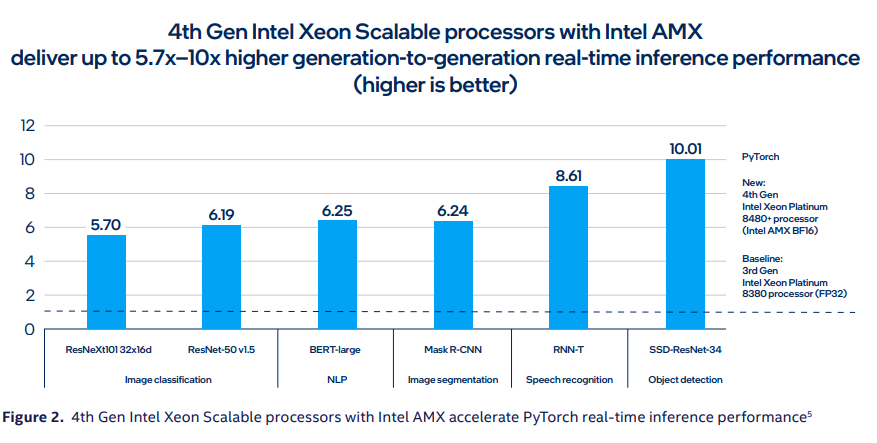
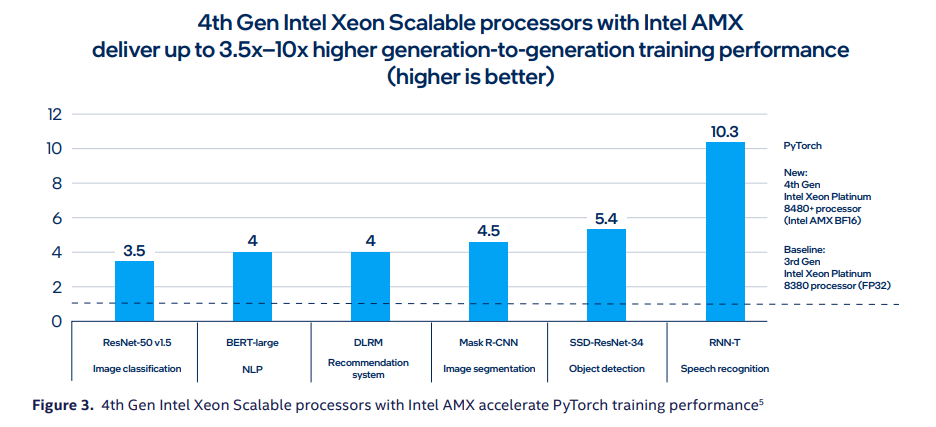
In the third generation there was an accelerator that took care of this aspect, the DL Boost (deep learning boost), the graphs below show how much performance has improved:
Would you like to know more?
Our sales engineers are at your disposal for any further information that may be useful. Contact us.